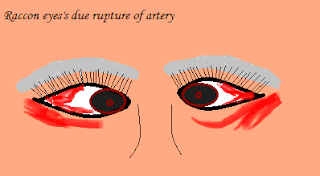
Panda sign / Raccon sign
It is called as peri orbital eccymosis.
indicate:
draining of blood down to the periorbital soft tissue due to fracture at the base of the skull.
It can be unilateral and bilateral suggest highly severe basalar fracture.
sign:
It may accompanied by battel sign .
They may not appear after 2-3 day if the injury.
Advice: