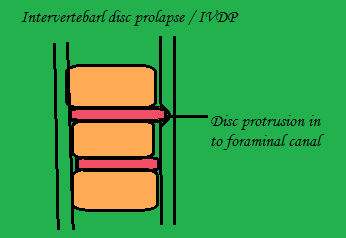
Intervertebral disc prolapsed Medical & Physiotherapy management
a) Medical management
- Rest
- Non anti-inflammatory Antipyretic drugs
b) Reduction
Bed rest and two weeks skin traction
if the pain is not reduced by corticosteroid injection
c) Chemonucleosis
Dissolution
of nucleuc pulposus by percutaneous injection of proteolytic enzyme.
b) Surgical Management
Hemi laminectomy
In this one side of the whole lamina
is removed
Laminectomy
In the spinous process both sides of
the lamina is removed.
Laminotomy
In the lamina a hole is made for
wider exposure
Fenestration
To expose the affected spinal canal,
the excise the ligamentum flavum bridging the two adjacent lamina
Indication
- No reduction in the symptoms of cauda equina
- Persistence pain and no reduction in sciatic tension after 3 weeks
- Neurological deterioration
PHYSIOTHERAPY MANAGEMENT
Before
planning for any function position to reduce pain should look for two bias:
Extension
bias: Patient
symptoms decrease in extension and provoked in flexion it shows a case of
intervertebral disc prolapsed.
Flexion
bias: Patient
symptoms are decrease in flexion and increase in extension that shows a case of
spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis.
Acute phase |
Aim
- To relieve patient from pain
- To promote muscle relaxation
- To reduce inflammatory sign
- Patient education
- Prevention
1.Controlled rest
- Postural correction by avoiding flexed posture
- prevent prolong / long time sitting with any back support
- Avoid heavy weight lifting object from the floor
- Advice the patient to use local support in form of corset:Lumbosacral belt, Abdominal blinder, Tap etc
- To prevent worsening of the symptoms, the patient is asked to take rest on a hard bed.
- Walking is advised to promote lumbar extension which will stimulate the fluid mechanism in the body to heal & reduce soft tissue swelling.
- If the patient present with inability to straighten up, make patient lie on prone position with 2-3 pillow under the abdomen. As the pain subside remove the pillow and place under the thorax, by this nucleus pulposus is shifted forwards and relieve pain and again lordosis
2.Use of modalities
- To reduce pain and Spasm: Moist pack is used
- To reduce Inflammation: Cryotherapy is done
- To relieve pain in acute and chronic phase: TENS is used
- To increase the extensibility of the connective tissue: Ultrasound is used
- To relieve nerve compression: Mechanical traction is used
3.Initial exercise in IVDP
- For posteriolateral protrusion:
Passive extension
Lateral shift correction
- For anteriolateral protrusion:
Passive flexion
Active ROM exercise
Maintain mobility
Patient education
Sub-acute phase |
- Same exercise in acute phase
- Cat and camel exercise: to emphasize on anterior pelvic tilt foe maintaining extension of spine
- Back isometrics exercise
Chronic phase |
a) Gentle active pain free ROM exercise
b) Stretching and flexibility exercise
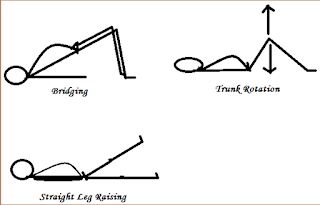 |
| back strengthening exercise |
c) Core stability exercise
- Abdominal curls
- Wall squat
- Straight leg raising
- Plank
- Side plank
d) Strengthening exercise
- Bridging
- Knee to chest
- Trunk rotation
- Back isometrics